Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues in the body.
Quick Links
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique that uses a magnetic field and computer-generated radio waves to create detailed images of the organs and tissues in the body. It is used for detecting brain tumors, traumatic brain injury, infections, stroke, dementia and root causes of headache.
An enormous amount of energy is required to create the magnetic fields for the imaging process. The heat load can change rapidly from 5 up to 80 kilowatts within minutes. Proper cooling is needed to enhance image performance and prevent disruptions during examination.
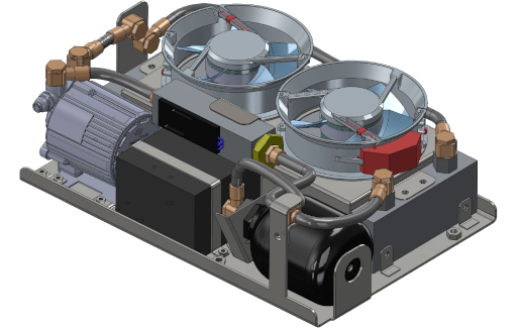
Custom liquid cooling systems
Given the higher efficiency compared to air-based heat transfer mechanisms, liquid cooling is the only option for MRI systems. Laird Thermal Systems has the capability to design liquid cooling solutions with cooling capacities of hundreds of kilowatts.