Optical Transceivers
Used to receive and transmit data, optical transceivers are key components of telecommunication networks.

Quick Links
Semiconductor lasers are the core element in transmitters for fiber-optic communication. The most common types of semiconductor laser transmitters used in fiber optics Fabry–Pérot, DFB and VCSEL. The choice of laser diode depends on the specific requirements of the telecom application, including distance, data rate, available bandwidth, power consumption, wavelength and the trade-offs between performance, cost, and reliability.
- Fabry-Perot (FP) laser diodes: commonly used in fiber-optic transmission systems as the light source for modulated optical signals
- Distributed feedback (DFB) laser diodes: use a grating structure that acts as a feedback mechanism to control the wavelength of the laser light. DFB laser diodes are used in applications that require a narrow and stable laser wavelength, such as dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) systems in optical communication networks
- Vertical cavity surface emitting lasers (VCSELs): type of surface-emitting laser diodes (SELs) that emit light vertically from the surface of the diode. VCSELs are used in applications that require low-cost, high-speed, and high-efficiency lasers, such as optical communication systems, data center interconnects, and fiber-optic sensing
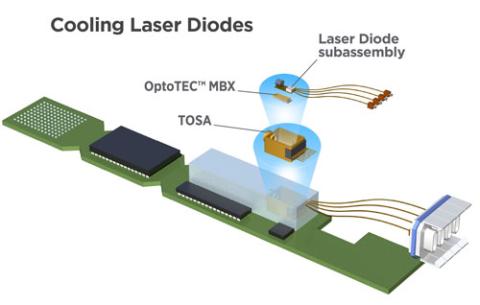
Temperature stabilization is a key challenge for wavelength stability in telecom applications. There are several methods used to regulate the temperature of a laser diode ( see all methods in our app note – link) TECs are an ideal technology for cooling laser diodes because they operate in bi-directional mode (cooling and heating) and provide high cooling power, fast response time, compact size, energy efficiency, low energy consumption and ease of temperature control.
Lasers for telecommunication applications have different packaging solutions, depending on the application area, data transmittance rates and types of transmitter-receiver systems. A few examples of commonly used diode packages for telecom applications include:
- Butterfly Package: The most common for lasers
- TOSA Package: a transmitter optical sub-assembly is used to convert the signal into an optical signal coupled into an optical fiber cable
- ROSA Package: a receiver optical sub-assembly receives an optical signal from a fiber and converts it back into an electrical signal
- BOSA Package: a bi-directional optical sub-assembly consists of both a TOSA and ROSA
- Pigtailed Package: provides a simple and straightforward optical connection, the package consists of a laser diode that is mounted onto a package with an optical fiber pigtailed
- Multi-Source Agreement (MSA) Package: designed to provide compatibility between different components and systems, making it easier to integrate laser diodes into a telecom network
For all these packages Laird Thermal Systems manufactures several different series of thermoelectric coolers:
The OptoTEC™ OTX/HTX Series miniature thermoelectric cooler. Designed for lower current and lower heat-pumping applications, the OptoTEC™ OTX/HTX Series Series keeps the laser diode operating temperature stable at around 25+/-0.5°C, achieving a temperature accuracy of ±0.01°C.
The OptoTEC™ MBX Series offers micro footprints as small as 1.6 x 1.6mm with thicknesses down to 0.9mm. The packing fraction for thermoelectric materials enables high heat pumping densities up to 43 W/cm2 at lower operating currents than traditional thermoelectric coolers.
To find your optimum thermal management solution for optical transceivers contact Laird Thermal Systems.
To learn more, see our related content.